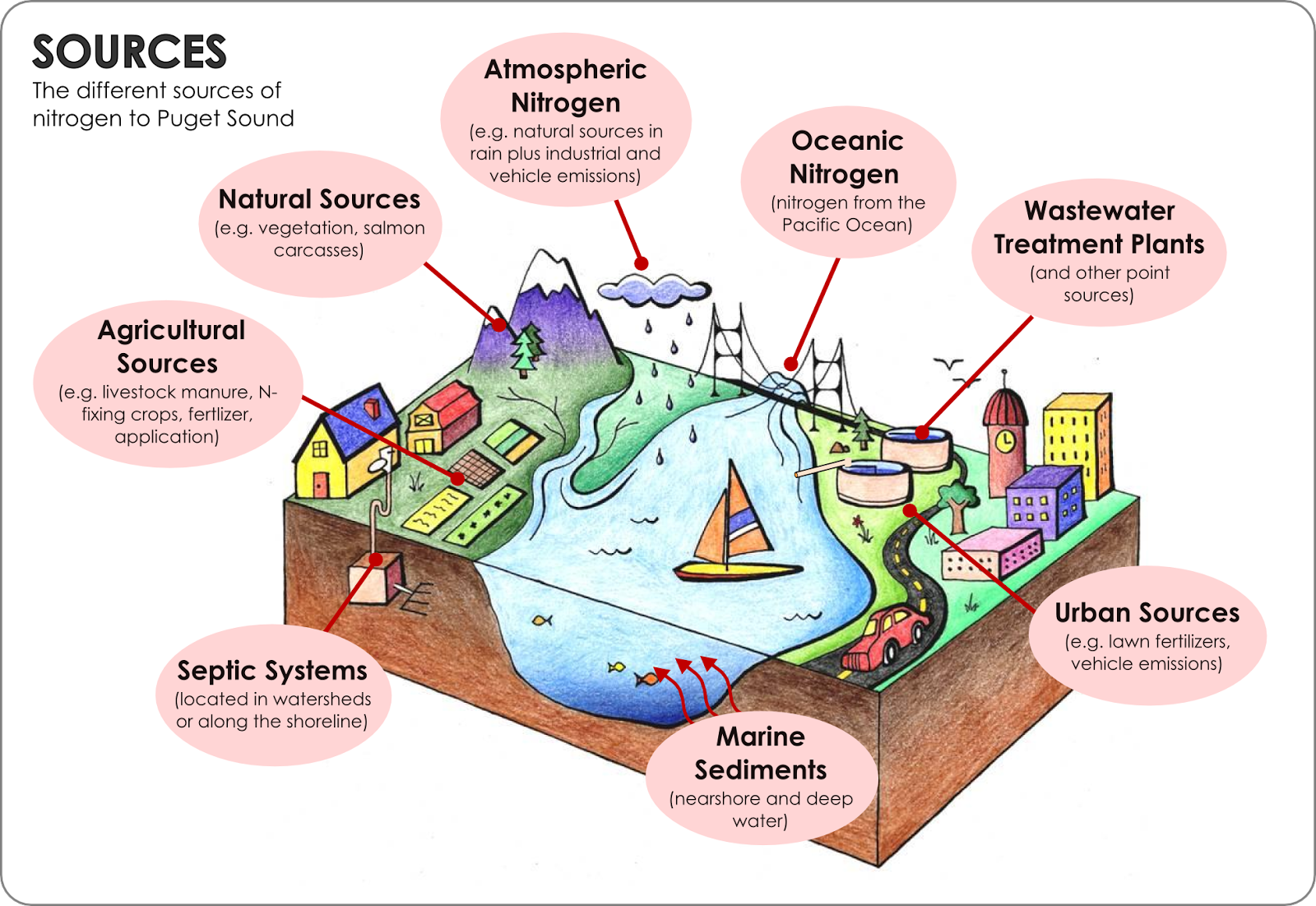
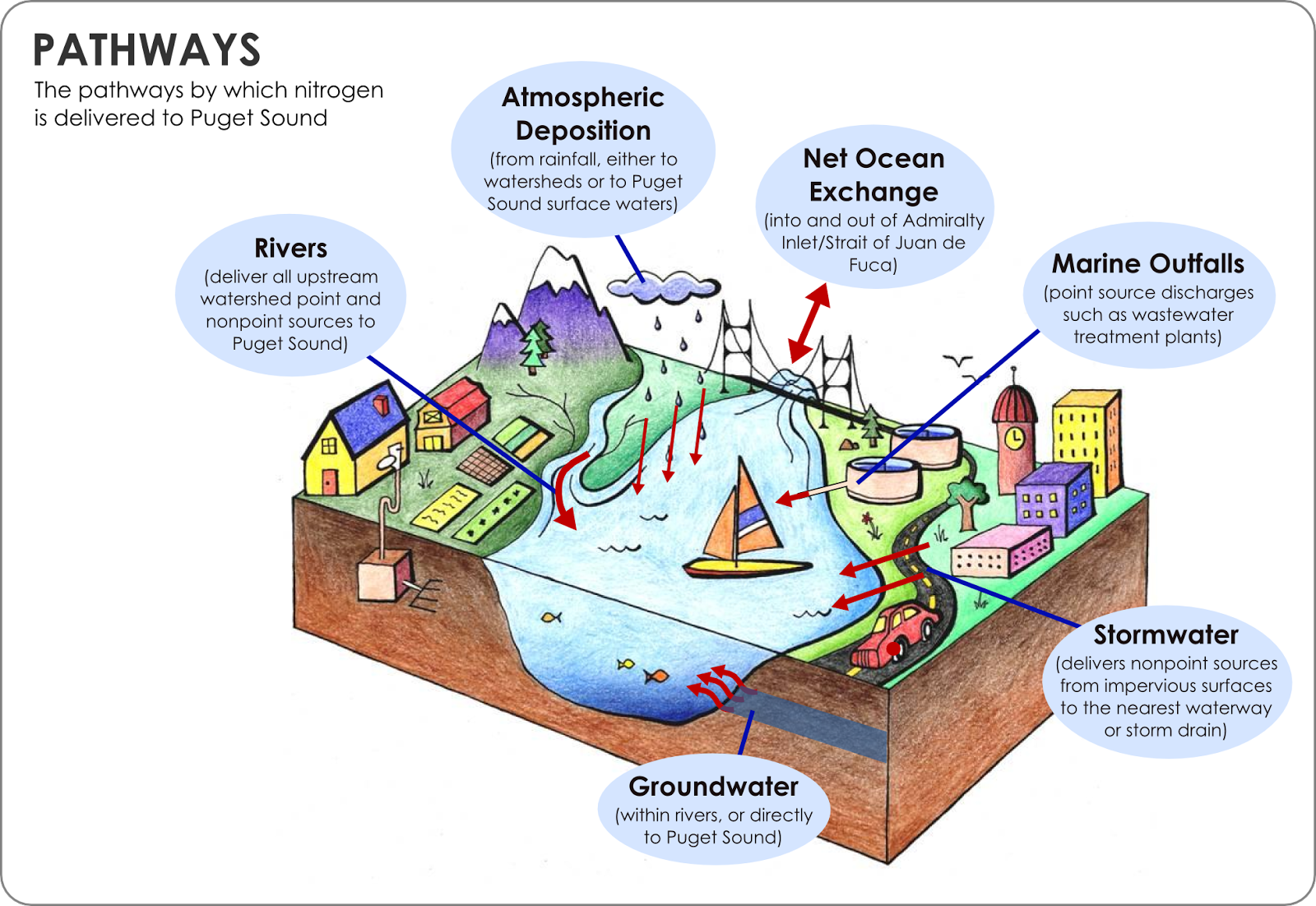
Two of our just-released scientific studies show the impacts of human nitrogen sources on dissolved oxygen in Puget Sound now and into the future:
- South Puget Sound Dissolved Oxygen Study: Water Quality Model Calibration and Scenarios
- Dissolved Oxygen Assessment for Puget Sound and the Straits: Impacts of Current and Future Human NitrogenSources and Climate Change through 2070
Impacts are greatest in parts of South and Central Puget Sound, although the Pacific Ocean has the largest influence overall.
We plan no regulatory changes as a result of the findings. Our next steps are to refine our analyses. We will continue to coordinate with cities, counties, tribes, and other stakeholders on next steps.
Oxygen matters…
Dissolved oxygen levels have been decreasing in Puget Sound. This is troubling because fish and other aquatic life need oxygen just like humans do. Fish use gills just like people use lungs — imagine how the low oxygen levels on the top of Mount Rainier feel to climbers. Similarly, when oxygen levels in the water are not high enough, fish can become stressed or die.
What’s causing the oxygen levels to decline? Is it us?
We began asking these questions in the late 1990s, but it wasn’t until recent computer model developments that we’ve been able to tease apart influences in the complex ecosystem of Puget Sound.
The Pacific Ocean is the largest source of nitrogen overall, but human activities add more through wastewater discharges and watershed inputs.
What’s the human footprint?
As the population grows in the region, wastewater inputs and developed lands increase. aily aDctivities generate more nitrogen, an essential element for growing plants, than a forested area does. Also, nitrogen is added through wastewater treatment plants and septic systems, as well as in runoff from fertilizers and domestic animals.
When too much nitrogen (which is a fertilizer) is added, excess algae blooms in marine waters like Puget Sound. That algae dies and decays, using up oxygen in the process.
Both studies found that these actions do worsen oxygen in some regions. Low oxygen is predominantly influenced by ocean inputs and local circulation patterns.
We also projected oxygen into the future — to the year 2070, when our region’s population will nearly double from 4.2 million people today to about 8 million. That means more wastewater, more developed lands, and more nitrogen.
Where are tje biggest impacts on oxygen?
While the biggest nutrient sources are from our biggest cities where most of people live, resulting impacts are showing up miles away. The South Sound study found that Carr, Case, Totten, Eld, and Budd Inlets in South Puget Sound, as well as East Passage in Central Puget Sound, respond the most to nitrogen inputs.
We also looked at the effect of human nitrogen sources throughout the U.S. and Canadian waters of the Salish Sea. Again, the greatest impacts were found in South and Central Puget Sound, both now and into the future. Circulation patterns make the South Sound a zone where ocean and human nutrients and their impacts get concentrated.
What about the ocean? How much of an impact does it have?
Pacific Ocean oxygen concentrations have been declining over a 50-year period. If those trends continue through 2070, oxygen levels would decline strongly in the Strait of Juan de Fuca, Strait of Georgia, and Hood Canal. We’re interested in what’s behind the ocean trends.
Climate change affects oxygen as well
Air temperatures will increase in the future, also warming the water. Warmer water holds less oxygen, so oxygen levels would decline further. This effect shows up strongest in shallow areas like Bellingham Bay.
The amount and timing of flow from the rivers will also change due to changing snowmelt. This speeds up or slows down circulation and brings in more or less nitrogen to Puget Sound at different times of the year.
What are the next steps?
These are the first detailed analyses of how Puget Sound oxygen concentrations respond to our activities, ocean conditions, and climate change. Other regions like Chesapeake Bay and the Gulf of Mexico have been evaluating these questions for decades.
We’ve clearly learned a great deal about how Puget Sound works. Over the next few years, we will improve and refine our computer prediction models. We will focus our effort on improving key processes such as bottom sediment influences.
We do not yet know whether reductions in human sources will be needed to meet water quality standards for dissolved oxygen. It is too early for regulatory changes. The next updates will be in 2015.
Thanks to staff, funding, and perseverance
These two studies provide a strong technical foundation for understanding a complex topic like dissolved oxygen in Puget Sound. Dozens of staff from Ecology, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, UW Climate Impacts Group, and partners have contributed to this work over the years — check out our website for a full list of publications and acknowledgments.
We lend a huge thanks to numerous monitoring and modeling staff and managers in Ecology’s Environmental Assessment and Water Quality Programs, who worked through science and policy questions for the past eight years.
And we thank more than 40 cities, counties, tribes, and other partners who provided insight and recommendations on numerous presentations and publications.
Lastly, we would not have achieved these accomplishments without funding support from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency under several National Estuary Program grants.
2020 Updates